 |
Viewing the Categorical Converter
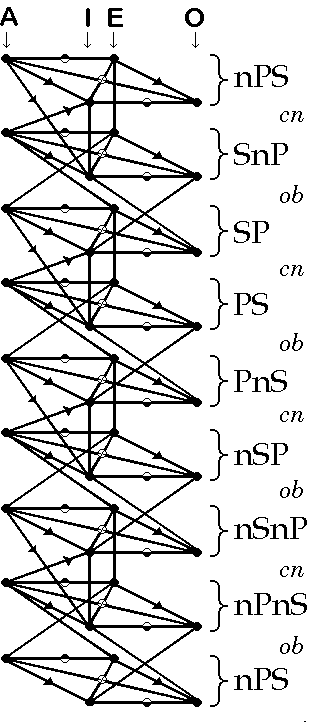 Black dots (
Black dots ( )
are propositions. On the diagram, locate the premise and
conclusion of your inference. )
are propositions. On the diagram, locate the premise and
conclusion of your inference.
You have three types of tokens: T (true),
F (false), and U (undetermined).
If the premise is true, place a true (T) token
on the dot which represents the premise. If it is
false, place a false (F) token on the dot.
Any path ( may join the premise and the conclusion. Move the token
from the premise to the conclusion, following
the paths, exchanging it according to the following rules:
may join the premise and the conclusion. Move the token
from the premise to the conclusion, following
the paths, exchanging it according to the following rules:
U is never exchanged.
If you have a T token, then:
- If you cross a contradiction (
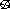 ) or contrary
( ) or contrary
( )
symbol, exchange the T token for an F. )
symbol, exchange the T token for an F.
- If you cross a subcontrary
(
 )
symbol, exchange the T token for a U. )
symbol, exchange the T token for a U.
- If you cross an arrow
(
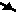 )
pointing against your direction of travel, exchange
the T token for a U. )
pointing against your direction of travel, exchange
the T token for a U.
If you have a F token, then:
- If you cross a contradiction (
 ) or subcontrary
( ) or subcontrary
( )
symbol, exchange the F token for a T. )
symbol, exchange the F token for a T.
- If you cross a Contrary
(
 )
symbol, exchange the F token for a U. )
symbol, exchange the F token for a U.
- If you cross an arrow
(
 )
pointing toward your direction of travel, exchange
the F token for a U. )
pointing toward your direction of travel, exchange
the F token for a U.
When moving from the premise to the conclusion,
you must avoid exchanging your token for a U
if at all possible.
The value of the token when it rests on the conclusion
is the result of the inference.
From here, you may learn
how to use the Categorical
Converter or learn how it was
constructed.
10 August 1996
|